Products
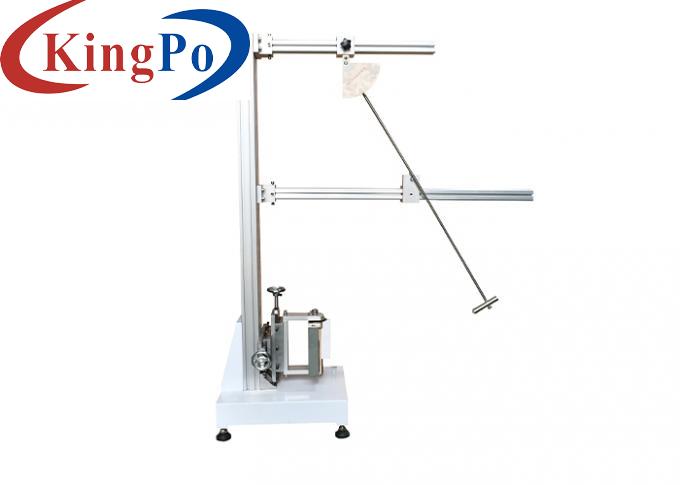

IEC 60068-2 Vertical Low Energy Pendulum Impact Test Device For Plugs And Sockets
Products Description
IEC 60068-2 Vertical Low Energy Pendulum Impact Test Device For Plugs And Sockets
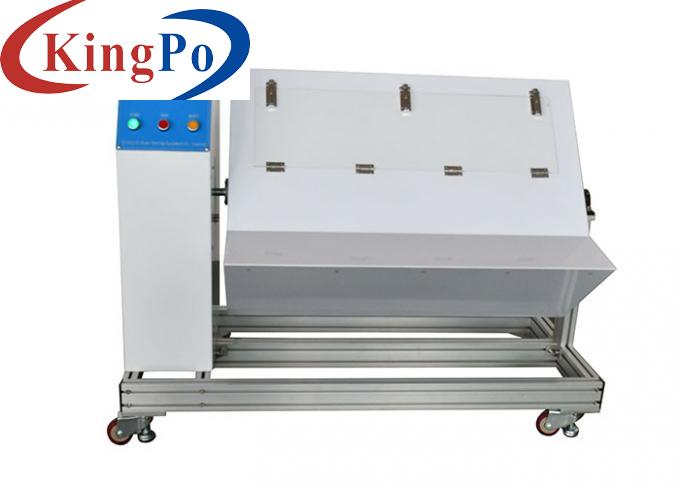
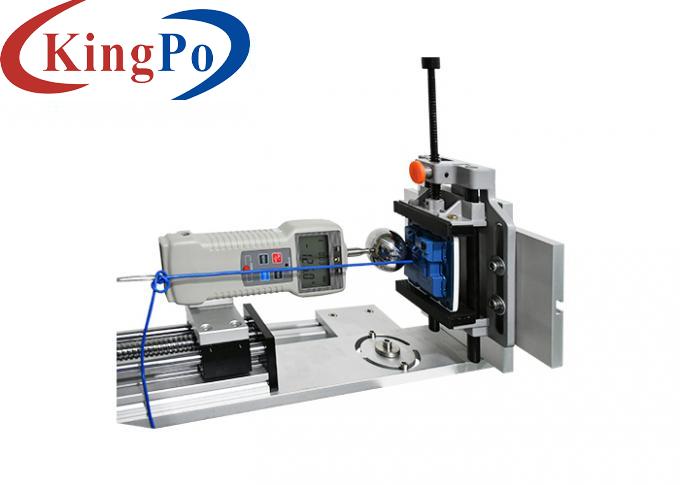
Product Overview For Vertical Low Energy Pendulum Impact Test Device:
This device is designed and manufactured according to the standard of IEC 60884-1:2022, IEC60068-2-75, and etc.
Sample: It is suitable for the mechanical strength test of electrical accessories such as plugs and sockets for household and similar purposes, surface-mounted installation boxes, threaded glands, covers, switches, etc.
Test Principle For Vertical Low Energy Pendulum Impact Test Device:
The test device is mainly composed of a pendulum whose upper end can be kept swinging in a vertical plane around its pendulum axis. The axis of the pendulum is 1000 mm above the measuring point. The pendulum consists of a rigid pendulum shaft and a compliant striking element. For heavier, bulky or difficult-to-handle test samples, a hand-held pendulum can be used for testing. This device is a low-energy pendulum impact device below 2J. It should be fixed vertically on a solid wall. The mounting bracket can be adjusted back and forth, left and right, and the impact height can be adjusted.
Technical Parameters For Vertical Low Energy Pendulum Impact Test Device:
1. Equivalent mass of impact element: 250g, 500g, 1.7Kg.
2. Position adjustment: bracket horizontal 150mm, vertical 150mm.
3. Pendulum shaft: a steel pipe with a length of 1000±1mm, an outer diameter of 9 mm, a wall thickness of 0.5 mm, and an outer diameter of 15.9 mm.
4. Swing shaft: Impact height: 65 mm, 80, 100 mm, 150 mm, 200 mm, 250 mm, 280, 400 mm scale display.
5. Install the wooden board (175*175*8mm.
6. Correspondence between drop height and energy.
Table 2 Drop height
Energy /J
0.14
0.2
(0.3)
0.35
(0.4)
0.5
0.7
1
2
5
10
20
50
Equivalent mass /kg
0.25
(0.2)
0.25
(0.2)
0.25
(0.2)
(0.2)
0.25
0.25
0.25
0.5
1.7
5
5
10
Drop height ±1%mm
56
(100)
80
(150)
140
(200)
(250)
200
280
400
400
300
200
400
500
Note 1. See Note 3.2.2; Note 2. The energy unit joule (J) in this part is derived from the standard gravitational acceleration (g), and the value of g is rounded to 10m/s².